Solar Panel Recycling Technologies: Sustainable Solutions
The Growing Need for Solar Panel Recycling Solar Panel Waste Management
Hey there, eco-conscious readers! So, you're probably thinking, "Solar panels? Aren't they supposed to be, like, the good guys?" Well, yeah, they are! They're a fantastic way to generate clean energy and reduce our reliance on fossil fuels. But here's the thing: solar panels don't last forever. After 25-30 years, they start to degrade and lose efficiency. And what happens then? They become waste. And we're talking about a LOT of waste as the solar industry continues to boom. That's where solar panel recycling comes in. It's super important that we have sustainable solutions for dealing with end-of-life solar panels to minimize environmental impact and recover valuable materials.
Current Solar Panel Recycling Methods Silicon Based Solar Panels
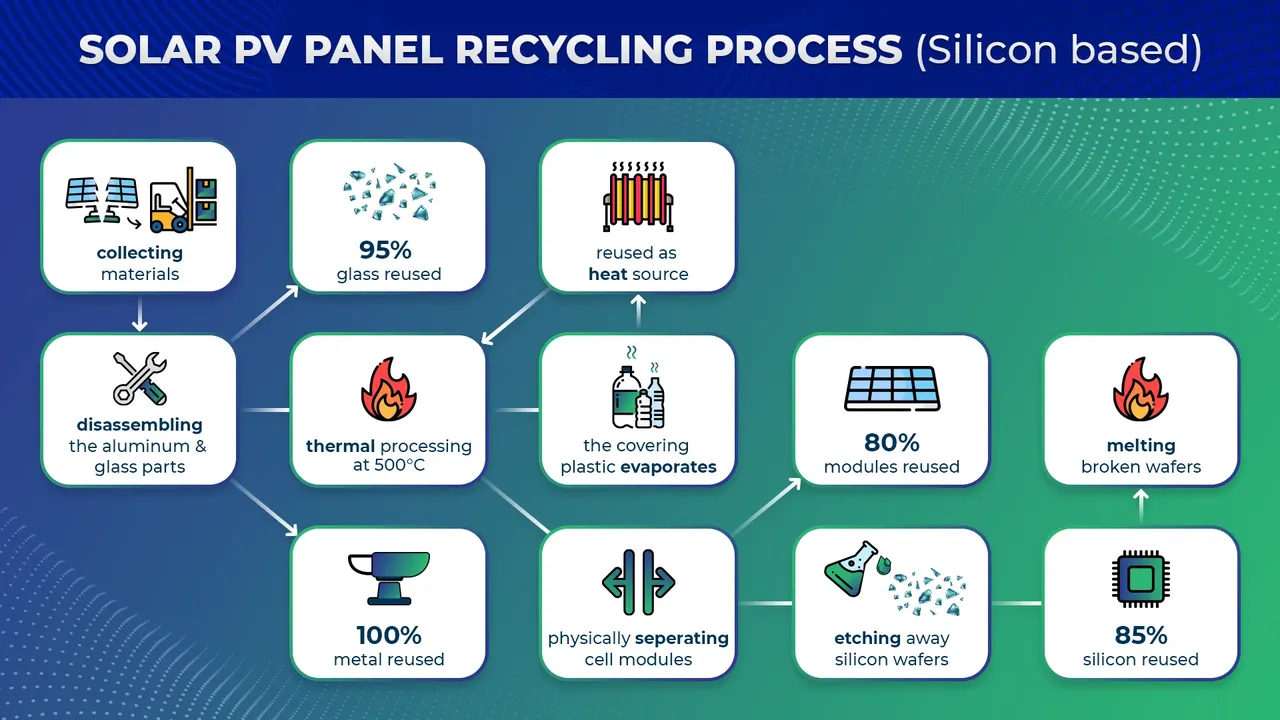
Okay, let's dive into how solar panels are actually recycled. The process isn't exactly like tossing your aluminum cans in the blue bin. It's a bit more complex. Most solar panels are silicon-based, and recycling them involves a few key steps:
- Panel Disassembly: First, the panels are taken apart. This means removing the aluminum frame, junction box, and cables. These components can often be recycled separately using standard methods.
- Glass Separation: The glass is separated from the silicon cells. This can be done mechanically or thermally. The glass is often recycled into new glass products, though sometimes it ends up as aggregate material. The quality of the recycled glass can vary depending on the process.
- Silicon Recovery: This is the tricky part! The silicon cells contain valuable materials like silicon, silver, and copper. There are different methods for recovering these materials, including chemical etching, thermal processing, and mechanical crushing. Each method has its pros and cons in terms of cost, efficiency, and environmental impact.
Advanced Recycling Technologies Thin Film Solar Panels
Now, silicon-based panels are the most common, but there's another type called thin-film solar panels. These panels use different materials, like cadmium telluride (CdTe) or copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS). Recycling these panels requires specialized processes due to the different materials involved.
- Chemical Leaching: Thin-film recycling often involves chemical leaching, where the panels are dissolved in a chemical solution to extract the valuable materials. This process needs to be carefully controlled to prevent environmental pollution.
- Material Recovery: The recovered materials, like cadmium and tellurium, can be reused in new thin-film solar panels or other applications. This helps to reduce the demand for virgin materials.
Product Recommendations and Comparisons Solar Panel Brands
Alright, let's talk about some specific solar panels and their potential recycling scenarios. It's tough to predict exactly *how* a panel will be recycled in 25 years, as technology is always evolving. But we can look at the materials used and the manufacturer's commitment to sustainability.
1. SunPower Maxeon Panels: SunPower panels are known for their high efficiency and durability. They use monocrystalline silicon cells. SunPower has a strong commitment to sustainability and offers a panel recycling program. While the specific recycling process might vary, the high value of the silicon and other materials makes them a good candidate for efficient recycling. Expect to pay a premium for SunPower panels, typically around $3-$4 per watt installed. Ideal for residential rooftops where space is limited and maximum power generation is needed.
2. First Solar Series 6 Panels: First Solar specializes in thin-film cadmium telluride (CdTe) panels. They have a well-established recycling program and claim a high recovery rate for CdTe. This is a big advantage for First Solar, as they take responsibility for the end-of-life management of their products. First Solar panels are generally more affordable than SunPower, around $2-$3 per watt installed. They're often used in large-scale solar farms due to their cost-effectiveness.
3. LG NeON Panels: LG offers high-performance monocrystalline silicon panels. While they may not have a dedicated recycling program as comprehensive as First Solar, the silicon and other materials in their panels are valuable and can be recycled using existing silicon-based recycling methods. LG panels are priced similarly to SunPower, around $3-$4 per watt installed. They are a good choice for homeowners looking for a balance of performance and reliability.
Comparison Table:
| Panel Brand | Technology | Recycling Program | Price per Watt (Installed) | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SunPower | Monocrystalline Silicon | Yes | $3-$4 | Residential Rooftops |
| First Solar | Cadmium Telluride (CdTe) | Yes (Comprehensive) | $2-$3 | Solar Farms |
| LG | Monocrystalline Silicon | No (Relies on existing silicon recycling) | $3-$4 | Residential Rooftops |
The Economics of Solar Panel Recycling Cost Benefit Analysis
Okay, let's be real. Recycling isn't always cheap. It costs money to collect, transport, and process solar panels. The economics of solar panel recycling depend on a few factors:
- Material Prices: The value of the recovered materials, like silicon, silver, and copper, affects the profitability of recycling. If these materials are selling for high prices, recycling becomes more attractive.
- Recycling Technology: The cost and efficiency of the recycling technology used play a big role. More advanced and efficient technologies can lower the cost of recycling.
- Government Regulations: Government policies, like subsidies or mandates, can incentivize solar panel recycling and make it more economically viable.
- EPR (Extended Producer Responsibility): EPR schemes hold manufacturers responsible for the end-of-life management of their products. This can encourage manufacturers to design panels that are easier to recycle and to invest in recycling infrastructure.
Right now, the economics of solar panel recycling are still evolving. In some cases, it may be cheaper to landfill panels than to recycle them. But as material prices rise, recycling technologies improve, and government regulations tighten, solar panel recycling is becoming increasingly economically viable.
The Environmental Benefits of Solar Panel Recycling Reducing Landfill Waste
Okay, so the economics might be a bit complicated, but the environmental benefits of solar panel recycling are clear. Here's why it's so important:
- Reducing Landfill Waste: Landfilling solar panels takes up valuable space and can potentially leach harmful materials into the environment. Recycling prevents these panels from ending up in landfills.
- Conserving Resources: Recycling recovers valuable materials that can be reused in new products, reducing the need to mine for virgin materials. This saves energy and reduces environmental impact.
- Reducing Pollution: Manufacturing new materials from scratch can be energy-intensive and polluting. Recycling reduces the need for these processes, lowering pollution levels.
- Promoting a Circular Economy: Solar panel recycling helps to create a circular economy where materials are reused and recycled, minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency.
Challenges and Opportunities in Solar Panel Recycling Future Trends
So, what are the challenges and opportunities in the world of solar panel recycling?
Challenges:
- Lack of Infrastructure: There's a need for more recycling facilities and infrastructure to handle the growing volume of end-of-life solar panels.
- Complex Recycling Processes: Recycling solar panels can be technically challenging and expensive.
- Varying Panel Designs: Different panel designs and materials can make recycling more difficult.
- Lack of Standardization: There's a need for more standardization in recycling processes and material recovery.
- Public Awareness: Many people are not aware of the importance of solar panel recycling.
Opportunities:
- Technological Innovation: There's a lot of potential for developing new and more efficient recycling technologies.
- Policy Support: Government policies can play a crucial role in promoting solar panel recycling.
- Business Opportunities: Solar panel recycling is a growing industry with opportunities for entrepreneurs and investors.
- Increased Awareness: Raising public awareness about the importance of solar panel recycling can drive demand for these services.
- Creating a Circular Economy: Solar panel recycling can contribute to a more sustainable and circular economy.
The Future of Solar Panel Recycling Innovation and Sustainability
The future of solar panel recycling looks bright! With continued innovation, policy support, and increased awareness, we can create a sustainable system for managing end-of-life solar panels. This will help to ensure that solar energy remains a truly clean and sustainable energy source for generations to come.
Specific Product Examples and Scenarios
Let's get even more specific with product examples. Imagine a homeowner in California installing a 10kW solar system using SunPower Maxeon panels. After 25 years, those panels reach the end of their lifespan. Because SunPower has a recycling program, the homeowner can contact them to arrange for the panels to be collected and recycled. The recovered silicon and other materials can then be used to manufacture new solar panels or other electronic devices.
Now, picture a large solar farm in Arizona using First Solar Series 6 panels. When these panels reach the end of their life, First Solar takes responsibility for recycling them. Their CdTe recycling process allows them to recover a high percentage of the cadmium and tellurium, which can be used to manufacture new thin-film panels. This closed-loop system helps to minimize waste and conserve resources.
Finally, consider a homeowner in Massachusetts installing LG NeON panels. While LG doesn't have a dedicated recycling program as comprehensive as SunPower or First Solar, the silicon and other materials in their panels can still be recycled using existing silicon-based recycling methods. The homeowner can contact a local recycling facility that specializes in electronics recycling to arrange for the panels to be recycled.
Pricing Considerations and Cost Analysis
The cost of recycling solar panels can vary depending on several factors, including the type of panel, the recycling method, and the location. Generally, recycling costs range from $10 to $30 per panel. However, as recycling technologies improve and the volume of end-of-life panels increases, these costs are expected to decrease.
It's important to factor in the cost of recycling when evaluating the overall cost of solar energy. While solar panels are a long-term investment, it's essential to consider the end-of-life management costs to ensure that solar energy remains a cost-effective and sustainable energy source.
Policy Recommendations for Solar Panel Recycling Government Initiatives
Government policies can play a crucial role in promoting solar panel recycling. Here are some policy recommendations:
- EPR (Extended Producer Responsibility) Schemes: Implement EPR schemes that hold manufacturers responsible for the end-of-life management of their products.
- Recycling Mandates: Establish recycling mandates that require a certain percentage of end-of-life solar panels to be recycled.
- Subsidies and Incentives: Provide subsidies and incentives to encourage solar panel recycling.
- Research and Development Funding: Invest in research and development to develop new and more efficient recycling technologies.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Launch public awareness campaigns to educate people about the importance of solar panel recycling.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/277019-baked-pork-chops-with-cream-of-mushroom-soup-DDMFS-beauty-4x3-BG-7505-5762b731cf30447d9cbbbbbf387beafa.jpg)