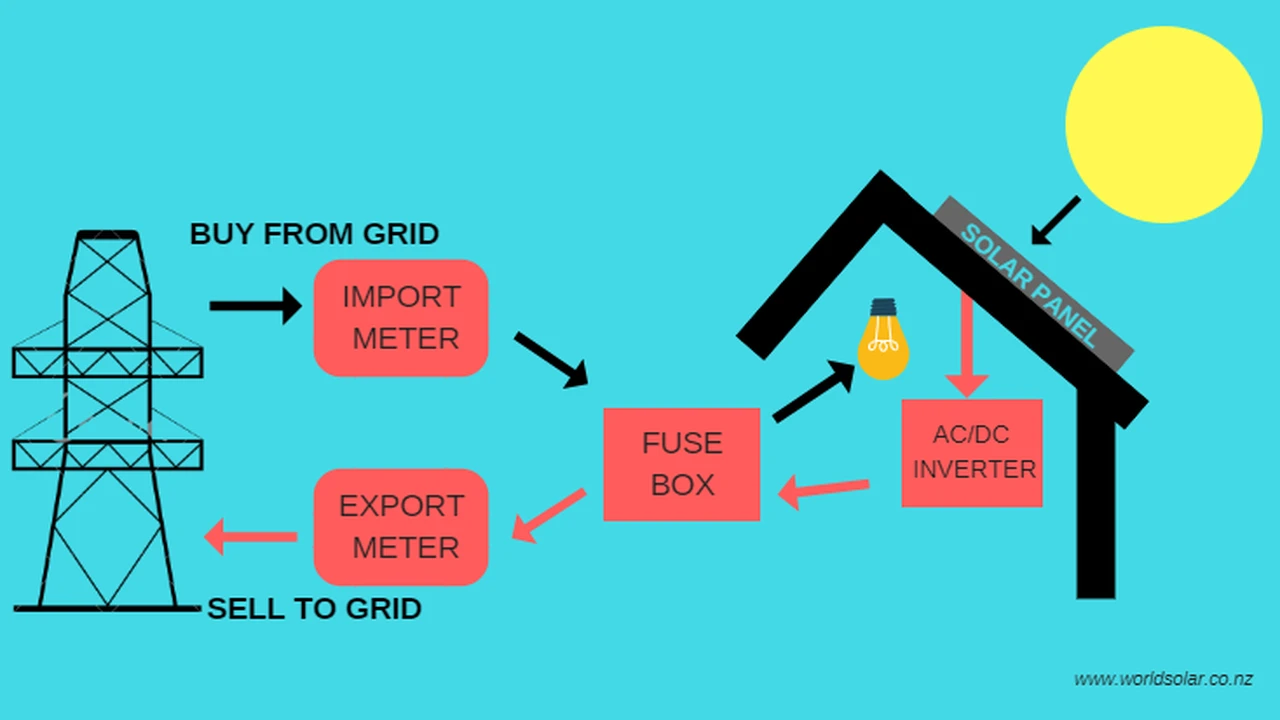
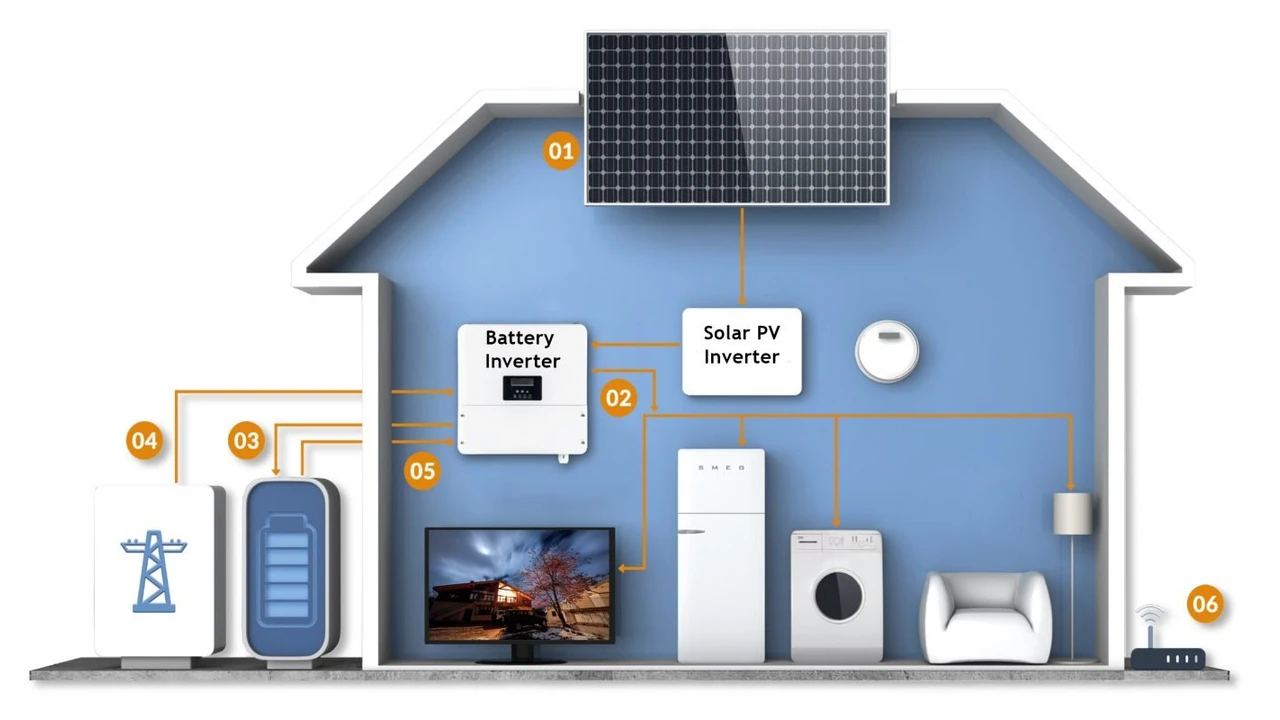
Solar Panel Environmental Impact: A Sustainable Choice

Understanding the Environmental Footprint of Solar Panels Solar Energy Environmental Benefits
Okay, so you're thinking about solar panels. Awesome! You're already on the path to a more sustainable lifestyle. But let's be real, nothing is *perfectly* green. Even solar panel production and disposal have an environmental impact. The good news is, compared to fossil fuels, solar is a clear winner. Let’s dive into why.
First off, when we talk about environmental impact, we're looking at a few key things: manufacturing, transportation, installation, operation, and end-of-life. Manufacturing solar panels requires energy and resources, including silicon, glass, and metals like aluminum and copper. This process can lead to greenhouse gas emissions and the use of water. Transportation also adds to the carbon footprint, especially if panels are shipped from overseas. Installation usually has a minimal impact. The operational phase is where solar really shines (pun intended!). Solar panels generate electricity with virtually no emissions during operation. Finally, end-of-life disposal or recycling is a growing concern, and thankfully, advancements are being made in this area.
So, how does this compare to fossil fuels? Well, burning coal, oil, and natural gas releases massive amounts of greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change, air pollution, and acid rain. The extraction, transportation, and processing of these fuels also have significant environmental impacts. Solar panels, on the other hand, significantly reduce these emissions over their lifespan. Studies show that solar energy can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 90% compared to fossil fuels.
Solar Panel Life Cycle Assessment Manufacturing Impacts and Sustainability
Let's break down the life cycle of a solar panel, starting with manufacturing. The process involves extracting raw materials, refining them, and assembling the panels. This requires energy, and depending on the energy source used in the manufacturing process (coal vs. renewable energy), the carbon footprint can vary significantly. For example, manufacturers in countries with strong renewable energy policies tend to have a lower environmental impact. Companies are also exploring ways to reduce their water usage and waste generation during manufacturing. Some are even using recycled materials in their panels.
One area of concern is the use of silicon. Silicon is the primary material used in most solar panels. Extracting and purifying silicon is energy-intensive. However, advancements are being made to use less silicon and improve the efficiency of the panels, which reduces the overall environmental impact.
Transparency is key. Look for manufacturers that are transparent about their environmental practices and have certifications like ISO 14001, which demonstrates a commitment to environmental management.
Solar Panel Installation and Environmental Considerations Rooftop Solar vs Ground Mounted Systems
The installation process is generally pretty straightforward. Rooftop solar panels have a smaller environmental footprint compared to ground-mounted systems because they don't require land clearing. Ground-mounted systems can have a larger impact if they require deforestation or disrupt sensitive ecosystems. When choosing a location for ground-mounted solar, it's important to consider the potential impact on the local environment. Avoid areas with valuable habitats or agricultural land. Some companies are even using solar farms to support pollinator habitats by planting native wildflowers around the panels.
The installation process itself usually involves minimal environmental disruption. However, it's important to choose a reputable installer that follows best practices for waste management and minimizes disturbance to the surrounding environment.
Operating Solar Panels Minimal Emissions and Renewable Energy Generation
This is where solar panels really shine! Once installed, solar panels generate electricity with virtually no emissions. They're powered by the sun, a clean and renewable energy source. This significantly reduces your reliance on fossil fuels and lowers your carbon footprint. The amount of electricity generated by solar panels depends on factors like sunlight intensity, panel efficiency, and the orientation of the panels. But even in cloudy climates, solar panels can generate a significant amount of electricity.
The environmental benefits of operating solar panels are undeniable. They reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve air quality, and conserve natural resources. By switching to solar, you're contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable future.
Solar Panel Recycling and End of Life Solutions Reducing Waste and Promoting Circular Economy
Okay, let's talk about the end of the road. Solar panels have a lifespan of around 25-30 years. What happens when they reach the end of their life? This is where recycling comes in. Recycling solar panels is a relatively new but rapidly growing industry. The goal is to recover valuable materials like silicon, glass, and metals, and reuse them in new products. This reduces the need to extract new resources and minimizes waste.
The challenge is that recycling solar panels can be complex and expensive. However, advancements are being made to make the process more efficient and cost-effective. Some companies are even developing innovative technologies to extract valuable materials from end-of-life solar panels. Look for manufacturers that offer take-back programs or partner with recycling companies to ensure that their panels are properly recycled at the end of their life.
While recycling is important, it's also crucial to design solar panels for durability and longevity. By extending the lifespan of solar panels, we can reduce the need for recycling and minimize waste.
Product Recommendations and Comparisons for Sustainable Solar Solutions
Alright, let's get down to brass tacks! You want some specific product recommendations, right? Here are a few options, keeping sustainability in mind:
REC Group Alpha Series
Use Case: Residential and commercial rooftop installations. These panels are known for their high efficiency and durability, even in challenging climates. They're a great choice if you want to maximize energy production in a limited space.
Comparison: Compared to standard polycrystalline panels, the REC Alpha series uses heterojunction technology (HJT), resulting in higher power output and better performance in high temperatures. They also have a lower temperature coefficient, meaning they lose less efficiency as temperatures rise.
Price: Expect to pay a premium for these panels, typically in the range of $3.00 - $3.50 per watt.
Panasonic EverVolt Series
Use Case: Residential installations. Panasonic's EverVolt series is known for its reliability and long-term performance. They come with a comprehensive warranty, giving you peace of mind.
Comparison: Panasonic panels are known for their low degradation rate, meaning they maintain a high level of performance over their lifespan. They also have a good track record for reliability and are less prone to failures compared to some other brands.
Price: These panels are also on the higher end, typically costing around $3.20 - $3.80 per watt.
SunPower Maxeon Series
Use Case: Residential and commercial installations where space is limited and high efficiency is paramount. SunPower panels are known for their industry-leading efficiency and durability.
Comparison: SunPower panels use a unique cell design that eliminates the need for grid lines on the front of the panel, resulting in higher efficiency and improved aesthetics. They also have a very low degradation rate and are backed by a long warranty.
Price: SunPower panels are the most expensive option, typically costing around $3.50 - $4.00 per watt.
Considerations When Choosing a Solar Panel
When choosing a solar panel, consider the following factors:
- Efficiency: How much sunlight can the panel convert into electricity? Higher efficiency panels will generate more power in a given space.
- Durability: How well will the panel withstand the elements? Look for panels with a strong warranty and a proven track record for reliability.
- Temperature Coefficient: How much does the panel's efficiency decrease as temperatures rise? A lower temperature coefficient is better.
- Warranty: What is the warranty coverage for the panel? A longer warranty provides more peace of mind.
- Environmental Impact: Consider the manufacturer's environmental practices and whether they offer recycling programs.
- Price: How much does the panel cost per watt? Balance price with performance and durability.
Solar Panel Applications and Scenarios Powering Homes Businesses and Beyond
Solar panels aren't just for rooftops anymore! They're being used in a wide range of applications, from powering homes and businesses to charging electric vehicles and even powering remote communities. Let's take a look at some common scenarios:
Residential Solar
This is the most common application of solar panels. Homeowners can install solar panels on their rooftops to generate electricity and reduce their reliance on the grid. Solar panels can also be used to power appliances, heat water, and even charge electric vehicles.
Commercial Solar
Businesses can also benefit from solar panels. By installing solar panels on their rooftops or on nearby land, businesses can reduce their energy costs and improve their sustainability. Solar panels can also be used to power factories, warehouses, and other commercial buildings.
Community Solar
Community solar projects allow multiple households or businesses to share the benefits of a single solar installation. This is a great option for people who don't own their homes or who don't have suitable rooftops for solar panels.
Off-Grid Solar
Solar panels can also be used to power homes and businesses that are not connected to the grid. This is a common application in remote areas where it's too expensive or impractical to connect to the grid. Off-grid solar systems typically include batteries to store energy for use when the sun isn't shining.
Solar Powered Transportation
Solar panels are also being used to power electric vehicles, boats, and even airplanes. Solar-powered transportation is a promising technology that could significantly reduce our reliance on fossil fuels.
So, there you have it! Solar panels are a sustainable choice with a growing number of applications. By understanding the environmental impact of solar panels and choosing the right products, you can contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable future. Do your research, talk to installers, and see if solar is right for you!
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/277019-baked-pork-chops-with-cream-of-mushroom-soup-DDMFS-beauty-4x3-BG-7505-5762b731cf30447d9cbbbbbf387beafa.jpg)